PowerShell Run Script
Running PowerShell scripts is a core part of automating administrative tasks in Microsoft 365 and Windows environments. Whether you're managing bulk user creation, license assignments, or system clean-ups, executing scripts correctly is crucial. Below are three common ways to run a PowerShell script, ranging from beginner-friendly to more professional approaches.
3 Different Ways for Running PowerShell Script
There are multiple methods to execute a PowerShell script, each suited for different experience levels and use cases. Let’s explore the three most popular options:
PowerShell Run Script Option One: Copy/Pasting the Code From the Script
This is the most primitive method. You simply open PowerShell, copy the script’s content, and paste it into the console.
# Example: Enable a user account
Update-MgUser -UserId "john.doe@domain.com" -AccountEnabled $true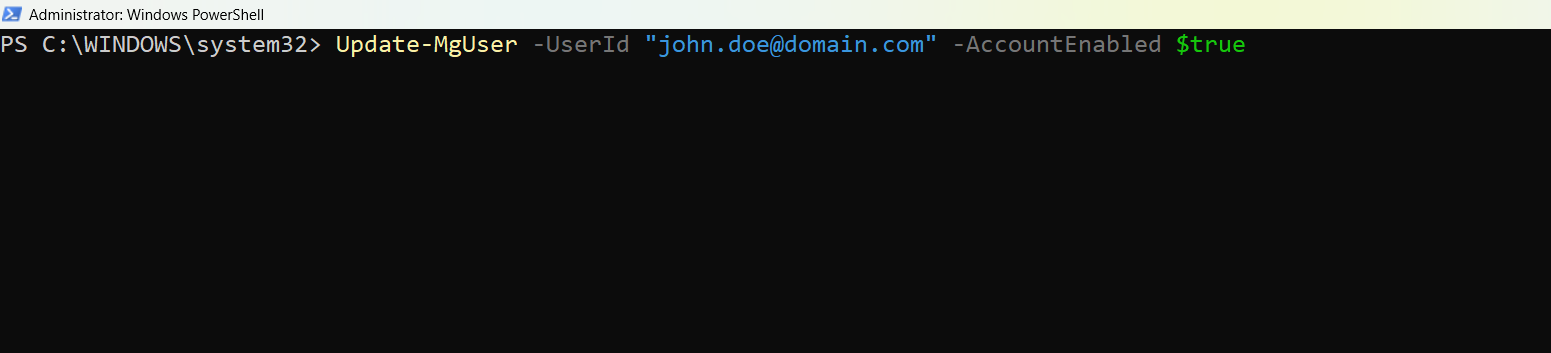
PowerShell Run Script Option Two: Executing .ps1 file From PS Console
This is the standard and recommended method for running reusable scripts.
- Save your script as a .ps1 file (e.g., CreateUsers.ps1)
- Open PowerShell.
- Navigate to the folder where the script is saved using cd.
- Run the script using: .\CreateUsers.ps1
.\CreateUsers.ps1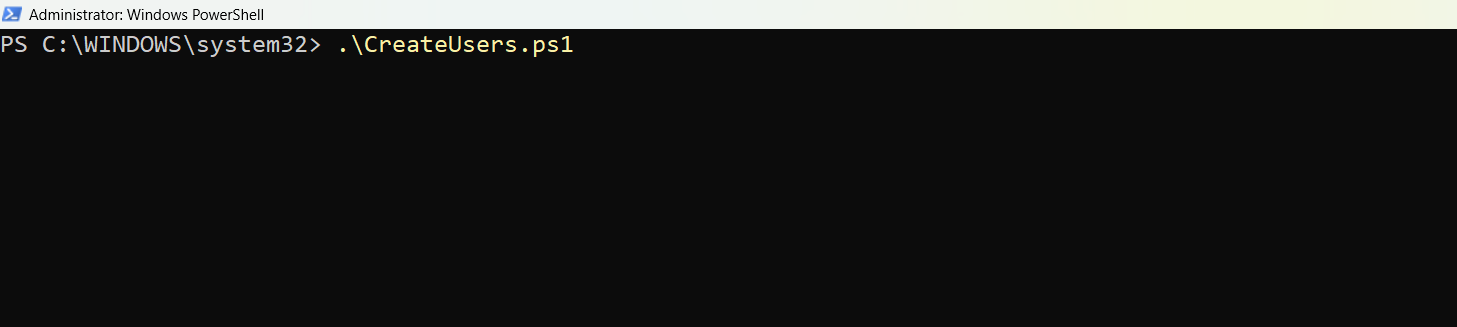
PowerShell Run Script Option Three: Executing the Script From Windows PowerShell ISE
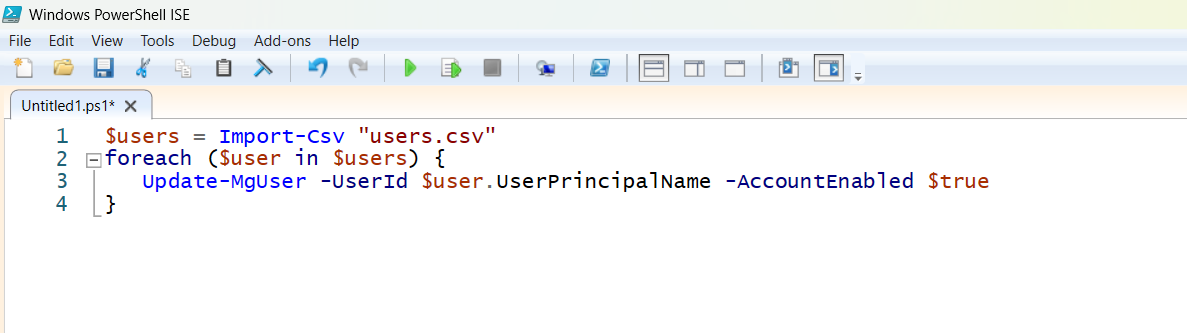
PowerShell ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) offers a graphical interface for writing, testing, and running scripts.
- Open PowerShell ISE.
- Paste or open your .ps1 file.
- Click Run or press F5. This method is beginner-friendly and excellent for debugging, though ISE is deprecated in favor of VS Code for advanced users.
Each method serves a purpose—choose the one that fits your task complexity and experience level. For repeated Microsoft 365 admin automation, saving and running .ps1 files is the most scalable approach.
Did You Know? Managing Microsoft 365 applications is even easier with automation. Try our Graph PowerShell scripts to automate tasks like generating reports, cleaning up inactive Teams, or assigning licenses efficiently.
Ready to get the most out of Microsoft 365 tools? Explore our free Microsoft 365 administration tools to simplify your administrative tasks and boost productivity.