Using Get-MgReportOffice365GroupActivityFileCount in Graph PowerShell
The Get-MgReportOffice365GroupActivityFileCount cmdlet is part of the Microsoft Graph PowerShell module and is used to generate reports on file activity within Office 365 Groups. Administrators can leverage this cmdlet to monitor file usage, ensure compliance, and optimize group storage management.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to using this cmdlet, with examples, usage tips, common errors and solutions, and use cases.
Cmdlet Syntax
Get-MgReportOffice365GroupActivityFileCount [-Period ] [-OutFile ] Parameters:
- -Period: Specifies the reporting period. Accepted values include
D7,D30,D90, andD180. If omitted, the cmdlet prompts for the value. - -OutFile: Specifies the path to save the report file. If omitted, the cmdlet prompts for this value.
Usage Examples
Example 1: Prompt-Based Input
This example runs the cmdlet without directly specifying -Period and -OutFile. The cmdlet will prompt for these values during execution.
Get-MgReportOffice365GroupActivityFileCountThe cmdlet prompts for:
- The
Periodparameter (e.g.,D7for the last 7 days). - The
OutFileparameter (e.g.,C:\Reports\GroupFileActivity.csv).
Once provided, the cmdlet generates the report and saves it to the specified location.
Example 2: Passing Parameters Directly
This example specifies both the -Period and -OutFile parameters directly in the command.
Get-MgReportOffice365GroupActivityFileCount -Period "D30" -OutFile "C:\Reports\GroupFileActivity.csv"The report for the past 30 days is generated and saved to C:\Reports\GroupFileActivity.csv.

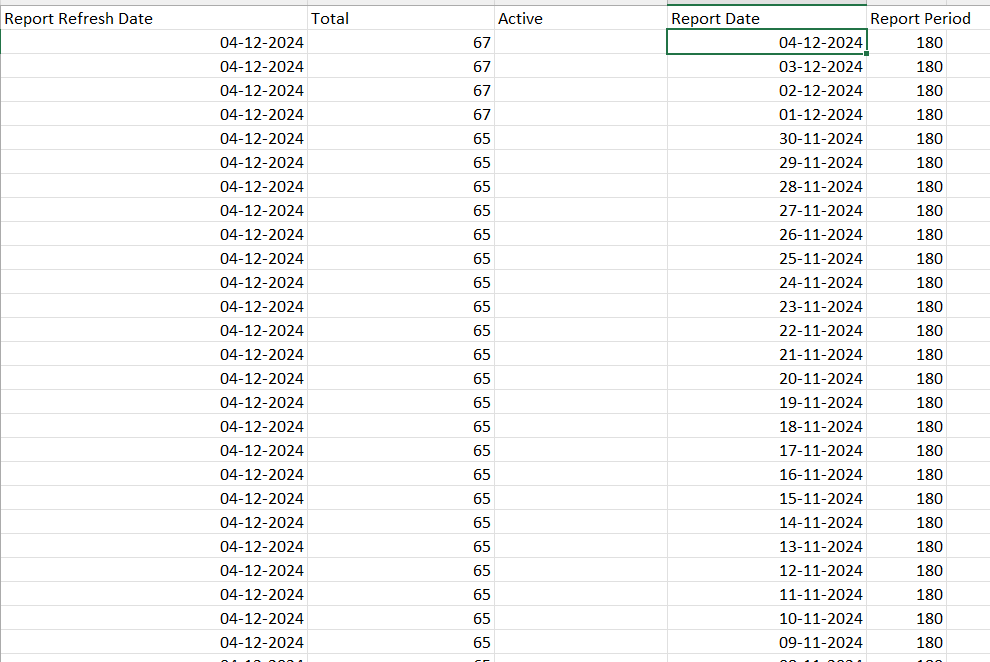
CSV Report With Its Headers
Cmdlet Tips
- Valid Period Values: The allowed values for the -Period parameter are
D7,D30,D90, andD180. Using values beyond these (e.g.,D180) will result in an error. - Graph Permissions: The cmdlet requires sufficient permissions. Ensure the account running the cmdlet has access to the Microsoft Graph Reports API.
- Large Reports: If fetching a large dataset (e.g., for
D180), ensure there is enough storage space at the specified -OutFile location.
Possible Errors and Solutions
| Error | Cause | Solution |
| Invalid Period Value | An unsupported value is provided to the -Period parameter. | Use only supported values: D7, D30, D90, or D180. |
| Access Denied | The user does not have the required permissions. | Assign the Reports.Read.All permission in Azure AD to the account. Grant admin consent if required. |
| Path Not Found | The specified path for the -OutFile parameter does not exist or is invalid. | Ensure the folder path exists before running the cmdlet. Use a valid file path format (e.g., C:\Reports\Report.csv). |
| File In Use | The output file is open or locked by another process. | Close any programs using the file and rerun the cmdlet. |
Use Cases
- File Activity Monitoring: Use the cmdlet to track file uploads, downloads, and edits across Office 365 Groups for a specific period.
- Compliance and Audit: Generate reports to ensure Office 365 Groups adhere to file storage and usage policies.
- Storage Optimization: Identify underused or inactive groups to optimize storage allocation.
- Group Management: Provide detailed file activity reports to group owners for better resource management.
Conclusion
The Get-MgReportOffice365GroupActivityFileCount cmdlet is a powerful tool for administrators to monitor file activity across Office 365 Groups. Its flexibility in defining reporting periods and exporting data makes it ideal for compliance, auditing, and optimizing storage. By understanding its usage, addressing common errors, and leveraging advanced filters, administrators can effectively manage group file activities.
Try these examples in your environment and share your feedback or suggestions for enhancing this process!