Track Conditional Access Policy Modifications Using Graph PowerShell
Conditional Access (CA) policies are critical to securing user access in Microsoft 365. These policies evolve over time to match changing security needs, but unaudited changes can lead to accidental exposure or misconfiguration.
Every time a Conditional Access policy is updated — whether it’s enabling/disabling the policy, changing assignments, or adjusting conditions — Azure AD logs this under the “Update policy” event in the “Policy” category.
In this article, you'll learn how to track CA policy modifications, identify who made the change, and determine when and what was modified using Graph PowerShell.
The Script: Query “Update policy” Events in Azure AD
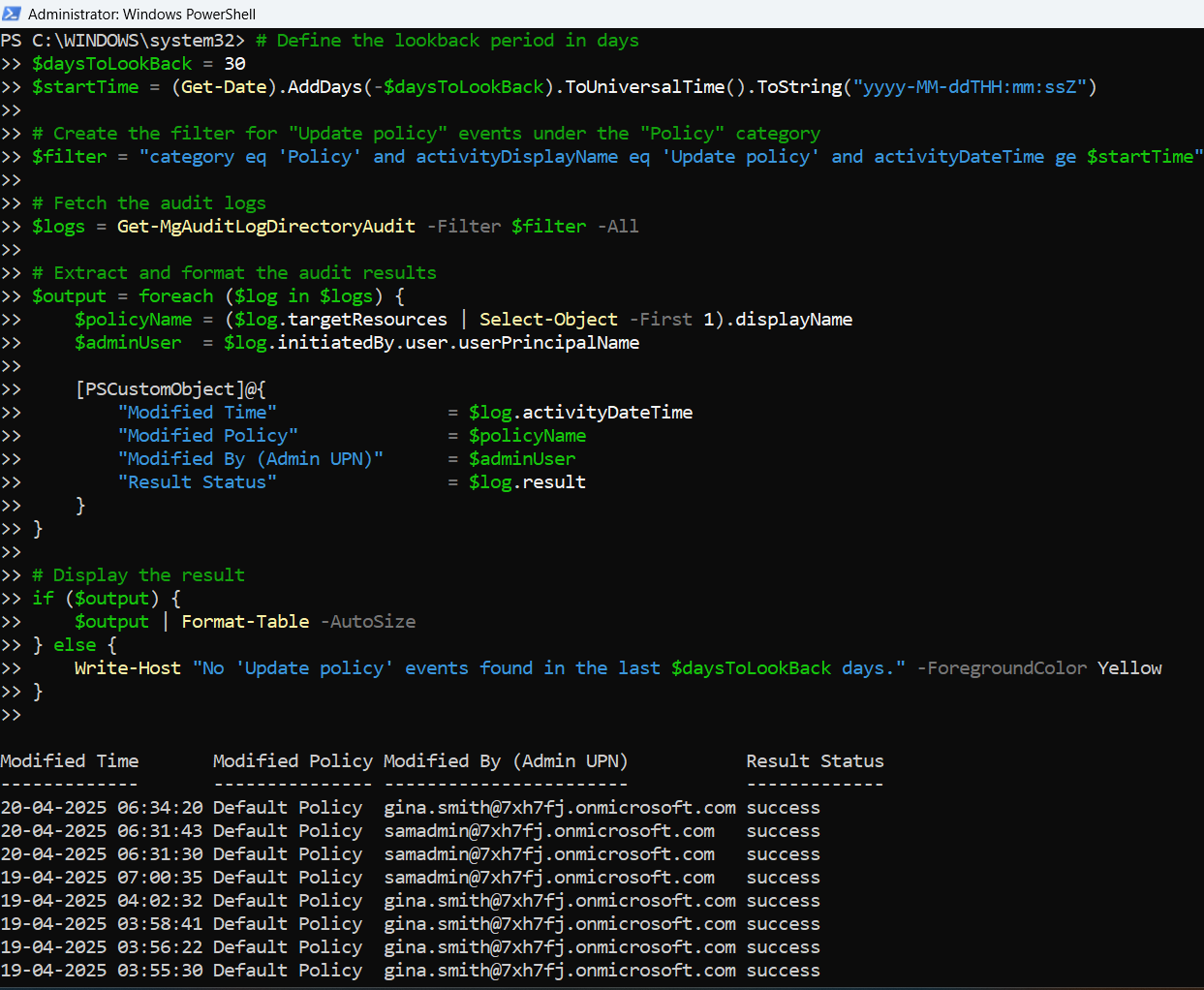
# Connect to Microsoft Graph
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes "AuditLog.Read.All"
# Define the lookback period in days
$daysToLookBack = 30
$startTime = (Get-Date).AddDays(-$daysToLookBack).ToUniversalTime().ToString("yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ")
# Create the filter for "Update policy" events under the "Policy" category
$filter = "category eq 'Policy' and activityDisplayName eq 'Update policy' and activityDateTime ge $startTime"
# Fetch the audit logs
$logs = Get-MgAuditLogDirectoryAudit -Filter $filter -All
# Extract and format the audit results
$output = foreach ($log in $logs) {
$policyName = ($log.targetResources | Select-Object -First 1).displayName
$adminUser = $log.initiatedBy.user.userPrincipalName
[PSCustomObject]@{
"Modified Time" = $log.activityDateTime
"Modified Policy" = $policyName
"Modified By (Admin UPN)" = $adminUser
"Result Status" = $log.result
}
}
# Display the result
if ($output) {
$output | Format-Table -AutoSize
} else {
Write-Host "No 'Update policy' events found in the last $daysToLookBack days." -ForegroundColor Yellow
}
How the Script Works
- Authentication
- Lookback Period
- Event Filtering
- category eq 'Policy'
- activityDisplayName eq 'Update policy'
- activityDateTime ge [lookback date in UTC ISO 8601 format]
- Data Extraction
- Modified Time – When the update occurred
- Modified Policy – Policy display name
- Modified By – Admin UPN who made the change
- Result Status – Whether the update succeeded or failed
It starts by connecting to Microsoft Graph using:
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes "AuditLog.Read.All"This scope allows access to Azure AD audit logs.
The script defines a variable $daysToLookBack, allowing you to audit policy updates over the past 7, 14, or 30 days.
Using OData, the script filters for:
It extracts:
Further Enhancements
- Export to CSV
Create a CSV log for long-term archiving:
$output | Export-Csv -Path "CA-Policy-Update-Audit.csv" -NoTypeInformationInvestigate changes made by a specific administrator:
$output | Where-Object { $_."Modified By (Admin UPN)" -eq "admin@domain.com" }$output | Where-Object { $_."Result Status" -ne "success" }Trigger notifications via email or webhook when unexpected policy changes are detected.
Possible Errors & Solutions
| Error | Cause | Solution |
| Invalid filter clause | Incorrect DateTime format | Use ToUniversalTime().ToString("yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ") |
| Access denied | Insufficient permission scope | Ensure the account has AuditLog.Read.All granted and consented |
| No matching audit logs | Filters are too narrow or time range is off | Widen your $daysToLookBack window or validate filter syntax |
Use Cases
- Change Management Tracking: Identify when CA policies were edited and by whom.
- Security Hardening Audits: Detect unauthorized or risky changes to security controls.
- Incident Response Review: Determine if a policy was modified during or after a security event.
- Delegated Admin Oversight: Monitor changes made by junior admins or third-party partners.
Conclusion
Conditional Access policies can make or break your organization’s security. Being able to audit every change ensures accountability, transparency, and compliance. This script gives you a clean, scriptable way to identify all modifications made to CA policies, helping you secure and govern your environment effectively.
With minimal effort, you can transform this into a scheduled report, real-time alerting system, or part of a change control pipeline.