🔧 New: User Management Graph PowerShell Toolkit
Simplify user tasks like bulk creation, updates, password resets, deletions, license checks & more — all from one place.
🚀 Launch ToolkitFetch and Email Microsoft 365 Users by Usage Location
Usage location plays a key role in Microsoft 365 management. It determines which services and licenses can be assigned to a user based on their geographical location. For instance, administrators may want to know all users set to a particular country code like US, IN, or GB for license auditing or compliance checks.
This Graph PowerShell script automatically fetches all users with a specified usage location, exports their details to a CSV report, and emails it to the administrator.
i) Script
$LocationCode = "US"
$AdminUPN = "admin@yourtenant.onmicrosoft.com"
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes "User.Read.All","Mail.Send"
$Users = Get-MgUser -All `
-Filter "usageLocation eq '$LocationCode'" `
-Property Id, DisplayName, UserPrincipalName, Mail, JobTitle, Department, AccountEnabled, UsageLocation
$ReportRows = $Users | Select-Object `
@{n='DisplayName'; e={$_.DisplayName}},
@{n='UserPrincipalName'; e={$_.UserPrincipalName}},
@{n='Mail'; e={$_.Mail}},
@{n='JobTitle'; e={$_.JobTitle}},
@{n='Department'; e={$_.Department}},
@{n='AccountEnabled'; e={$_.AccountEnabled}},
@{n='UsageLocation'; e={$_.UsageLocation}}
$ReportPath = "$env:TEMP\Users_By_UsageLocation_$LocationCode.csv"
$ReportRows |
Sort-Object DisplayName |
Export-Csv -Path $ReportPath -NoTypeInformation -Encoding UTF8
$userCount = @($ReportRows).Count
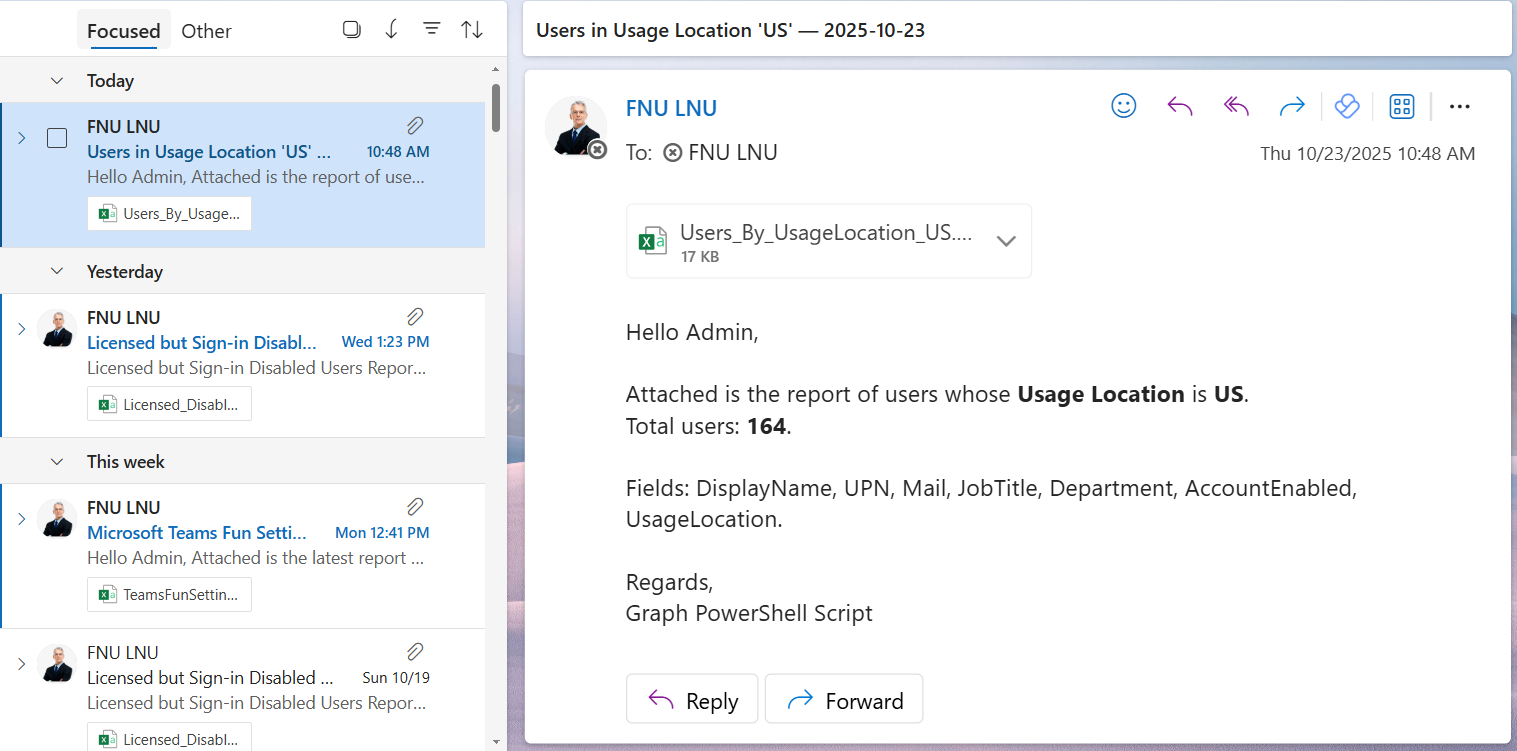
$Subject = "Users in Usage Location '$LocationCode' — $(Get-Date -Format 'yyyy-MM-dd')"
$Body = @"
Hello Admin,<br><br>
Attached is the report of users whose <b>Usage Location</b> is <b>$LocationCode</b>.<br>
Total users: <b>$userCount</b>.<br><br>
Fields: DisplayName, UPN, Mail, JobTitle, Department, AccountEnabled, UsageLocation.<br><br>
Regards,<br>
Graph PowerShell Script
"@
$AttachmentContent = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.IO.File]::ReadAllBytes($ReportPath))
$Attachments = @(
@{
"@odata.type" = "#microsoft.graph.fileAttachment"
Name = [System.IO.Path]::GetFileName($ReportPath)
ContentBytes = $AttachmentContent
}
)
$Message = @{
Message = @{
Subject = $Subject
Body = @{
ContentType = "HTML"
Content = $Body
}
ToRecipients = @(
@{ EmailAddress = @{ Address = $AdminUPN } }
)
Attachments = $Attachments
}
SaveToSentItems = "true"
}
Send-MgUserMail -UserId $AdminUPN -BodyParameter $Message
Write-Host "Usage Location '$LocationCode' users report emailed successfully to $AdminUPN"
ii) How the Script Works
- Configuration – The $LocationCode variable defines the target usage location (e.g., US). The $AdminUPN variable specifies the email address of the administrator who will receive the report.
- Graph Connection – The script connects to Microsoft Graph with two scopes: User.Read.All (to read user data) and Mail.Send (to email the report).
- Fetch Users – The Get-MgUser cmdlet retrieves all users whose usageLocation matches the provided country code.
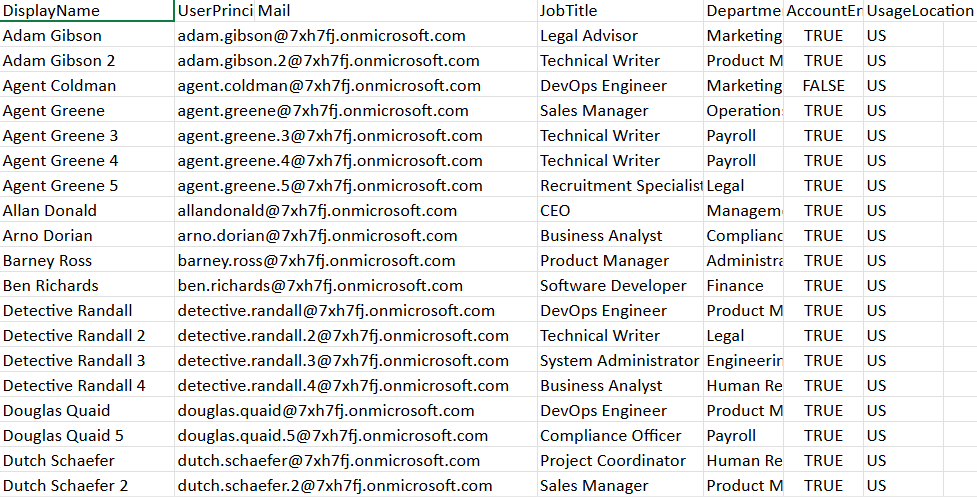
- Prepare the Data – The output includes user details such as DisplayName, UPN, Mail, JobTitle, Department, AccountEnabled status, and UsageLocation.
- Export to CSV – The data is sorted alphabetically by user name and exported to a CSV file in the system’s temporary folder.
- Email Delivery – The CSV file is then attached to an HTML-formatted email and sent to the administrator. The subject line and body include a summary of the total users found for the selected location.
iii) Further Enhancements
- Dynamic Location Input – Prompt the administrator to input the usage location interactively rather than hardcoding it.
- Multiple Location Support – Modify the script to generate separate reports for multiple country codes.
- Add Sign-In Activity – Extend the report to include SignInActivity or LastLoginDateTime for active/inactive analysis.
- Automation – Schedule the script using Task Scheduler or Azure Automation for periodic updates.
- Conditional Alerting – Add logic to send alerts if the number of users in a specific location exceeds a threshold.
iv) Possible Errors and Solutions
| Error | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Insufficient privileges to complete the operation | Missing or incorrect permissions. | Ensure the connection uses User.Read.All and Mail.Send scopes. |
| Send-MgUserMail : Resource not found | The admin mailbox specified in $AdminUPN is invalid or not mail-enabled. | Use a valid Microsoft 365 mailbox for the admin. |
| Empty CSV File | No users found with the specified usage location. | Verify the location code (e.g., US, IN, GB) and ensure users have the UsageLocation property set. |
| BadRequest from Get-MgUser | Incorrect filter syntax or quotation marks. | Always enclose $LocationCode in single quotes within the filter, like "usageLocation eq '$LocationCode'". |
v) Conclusion
This Graph PowerShell script makes it simple for administrators to identify users by usage location within Microsoft 365. By automating report generation and email delivery, it enhances both visibility and efficiency, helping admins perform license audits, regional compliance checks, or user distribution analysis effortlessly.
With a few enhancements—like adding automation or sign-in details—this script can evolve into a valuable asset for ongoing tenant management and auditing.