Bulk Remove Global Administrator Role Using Microsoft Graph PowerShell
Removing privileged roles such as Global Administrator is just as important as assigning them. Whether you’re cleaning up legacy access, enforcing least-privilege policies, or responding to an audit finding, doing this manually for multiple users can be tedious and error-prone.
In this article, we’ll walk through a tested Microsoft Graph PowerShell script that bulk removes the Global Administrator role from users read from a CSV file using the Remove-MgDirectoryRoleMemberByRef cmdlet.
⚠️ Important note:
This script only works with User Object IDs.
User Principal Names (UPNs) are not supported for directory role removal using this cmdlet.
🚀 Community Edition Released!
Try the M365Corner Microsoft 365 Reporting Tool — your DIY pack with 20+ out-of-the-box M365 reports for Users, Groups, and Teams.
i) The Script
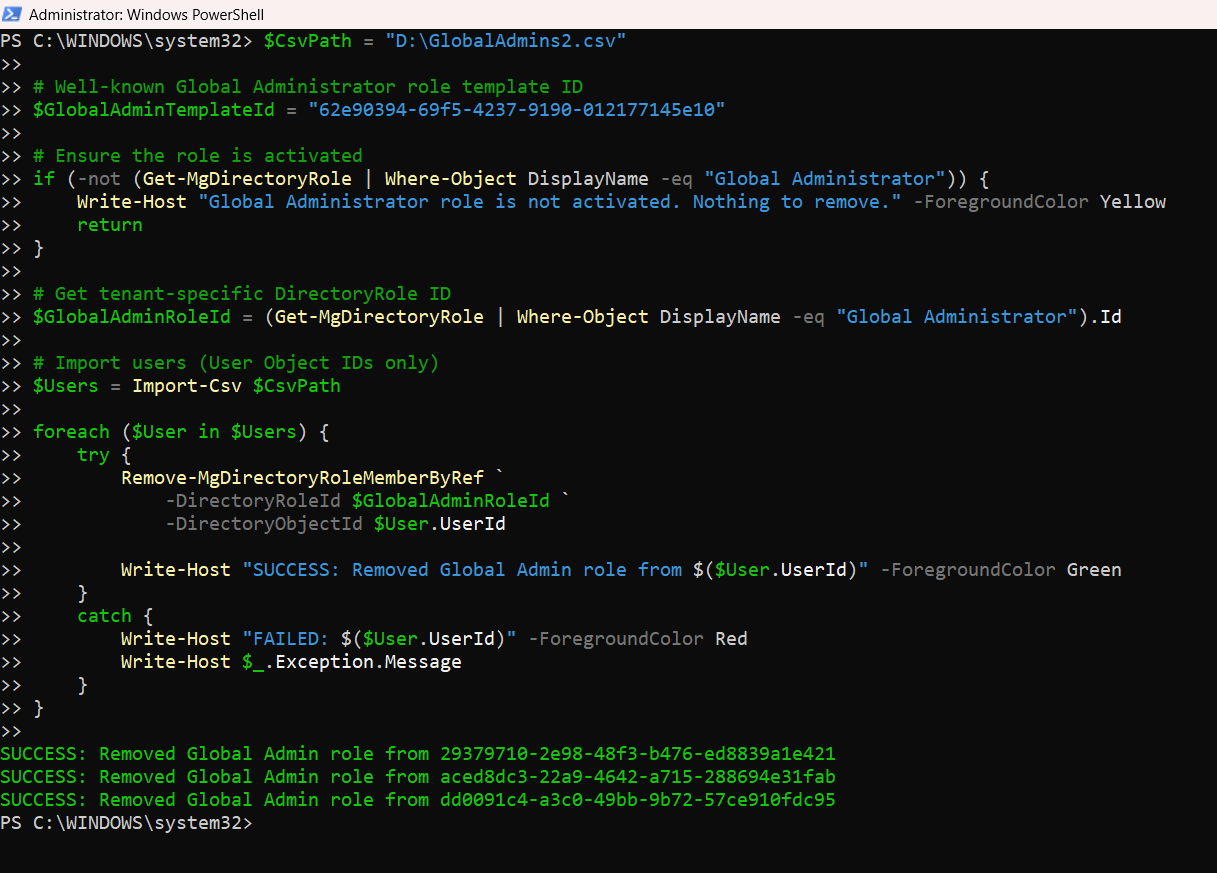
Below is the complete, working Graph PowerShell script for bulk removal of the Global Administrator role.
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes "RoleManagement.ReadWrite.Directory","Directory.Read.All"
$CsvPath = "C:\Temp\GlobalAdmins.csv"
# Well-known Global Administrator role template ID
$GlobalAdminTemplateId = "62e90394-69f5-4237-9190-012177145e10"
# Ensure the Global Administrator role is activated
if (-not (Get-MgDirectoryRole | Where-Object DisplayName -eq "Global Administrator")) {
Write-Host "Global Administrator role is not activated. No users to remove." -ForegroundColor Yellow
return
}
# Fetch the tenant-specific DirectoryRole ID
$GlobalAdminRoleId = (Get-MgDirectoryRole | Where-Object DisplayName -eq "Global Administrator").Id
# Import users from CSV (User Object IDs only)
$Users = Import-Csv $CsvPath
foreach ($User in $Users) {
try {
Remove-MgDirectoryRoleMemberByRef `
-DirectoryRoleId $GlobalAdminRoleId `
-DirectoryObjectId $User.UserId
Write-Host "SUCCESS: Removed Global Admin role from $($User.UserId)" -ForegroundColor Green
}
catch {
Write-Host "FAILED: $($User.UserId)" -ForegroundColor Red
Write-Host $_.Exception.Message
}
}
CSV File Format
The CSV file must contain User Object IDs.
UserId
18a80140-b0fb-4489-b360-2f6efaf225a0
86503198-b81b-43fe-81ee-ad45b8848ac9
⚠️ Using UPNs (for example, user@contoso.com) will result in errors.
ii) How the Script Works
Let’s break down the script logic step by step.
- Graph Connection and Permissions
- RoleManagement.ReadWrite.Directory
- Directory.Read.All
- Verifying Role Activation
- Resolving the Correct Role ID
- Reading Users from CSV
- Removing the Role Assignment
The script connects to Microsoft Graph with permissions required to manage directory roles:
Without these permissions, role removal will fail.
Directory roles in Entra ID must be activated before they can be managed.
The script checks whether the Global Administrator role exists in the tenant’s /directoryRoles collection.
If the role is not activated, the script exits gracefully since there would be no role members to remove.
Once confirmed, the script dynamically retrieves the tenant-specific DirectoryRole ID for the Global Administrator role.
This step is critical—role template IDs cannot be used with Remove-MgDirectoryRoleMemberByRef.
The script imports users from a CSV file containing User Object IDs only.
These IDs are required because Graph directory role operations rely on object references, not user principal names.
For each user, the script calls:
Remove-MgDirectoryRoleMemberByRef
Unlike role assignment, role removal does not use an @odata.id body.
Instead, the user’s object ID is passed directly via the -DirectoryObjectId parameter.
iii) Further Enhancements
This script can be extended in several useful ways:
- 🔍 Check if the user is a Global Admin before attempting removal
- 📄 Export success and failure results to a CSV log
- 🧪 Add a dry-run mode for audit validation
- 🔐 Integrate approval prompts for production environments
- ⏳ Replace permanent removal logic with PIM role deactivation workflows
Such enhancements are particularly useful in security-sensitive or audited tenants.
iv) Possible Errors and Solutions
| Error | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Request_ResourceNotFound (404) | The Global Administrator role is not activated in the tenant. | Activate the role before attempting removal or ensure it already exists. |
| Invalid object identifier | The CSV contains UPNs instead of User Object IDs. | Update the CSV to use user IDs retrieved from Entra ID. |
| Authorization_RequestDenied | Missing Microsoft Graph permissions. | Reconnect to Graph with:
|
| No output / no changes | The user is not currently assigned the Global Administrator role. | This is expected behavior; optionally add pre-validation logic. |
v) Conclusion
Bulk removal of privileged roles is a key part of maintaining a secure Microsoft 365 environment. By using Microsoft Graph PowerShell and dynamically resolving directory roles, administrators can safely remove Global Administrator access at scale without relying on manual portal actions.
This script provides a reliable, tenant-safe, and repeatable approach to role removal while adhering to Microsoft Graph’s strict role management requirements. As always, apply additional safeguards such as logging, approvals, and PIM where appropriate.